HttpRequest的QueryString属性 的一点认识
如:
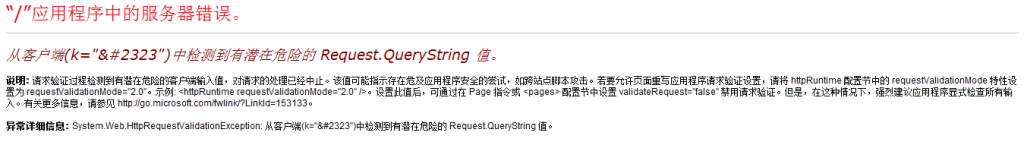
当然我们一般都是按照提示来把framework版本设置2.0来解决。为什么可以这么解决了,还有没有其它的解决方法了。
先让我们看看QueryString的源代码吧:
public NameValueCollection QueryString
{
get
{
if (this._queryString == null)
{
this._queryString = new HttpValueCollection();
if (this._wr != null)
{
this.FillInQueryStringCollection();
}
this._queryString.MakeReadOnly();
}
if (this._flags[1])
{
this._flags.Clear(1);
this.ValidateNameValueCollection(this._queryString, RequestValidationSource.QueryString);
}
return this._queryString;
}
}
private void FillInQueryStringCollection()
{
byte[] queryStringBytes = this.QueryStringBytes;
if (queryStringBytes != null)
{
if (queryStringBytes.Length != 0)
{
this._queryString.FillFromEncodedBytes(queryStringBytes, this.QueryStringEncoding);
}
}
else if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.QueryStringText))
{
this._queryString.FillFromString(this.QueryStringText, true, this.QueryStringEncoding);
}
}
先让我们插入一点 那就是QueryString默认已经做了url解码。 其中HttpValueCollection的 FillFromEncodedBytes方法如下
internal void FillFromEncodedBytes(byte[] bytes, Encoding encoding)
{
int num = (bytes != null) ? bytes.Length : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
string str;
string str2;
this.ThrowIfMaxHttpCollectionKeysExceeded();
int offset = i;
int num4 = -1;
while (i < num)
{
byte num5 = bytes[i];
if (num5 == 0x3d)
{
if (num4 < 0)
{
num4 = i;
}
}
else if (num5 == 0x26)
{
break;
}
i++;
}
if (num4 >= 0)
{
str = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(bytes, offset, num4 - offset, encoding);
str2 = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(bytes, num4 + 1, (i - num4) - 1, encoding);
}
else
{
str = null;
str2 = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(bytes, offset, i - offset, encoding);
}
base.Add(str, str2);
if ((i == (num - 1)) && (bytes[i] == 0x26))
{
base.Add(null, string.Empty);
}
}
}
从这里我们可以看到QueryString已经为我们做了解码工作,我们不需要写成 HttpUtility.HtmlDecode(Request.QueryString["xxx"])而是直接写成Request.QueryString["xxx"]就ok了。
现在让我们来看看你QueryString的验证,在代码中有
if (this._flags[1])
{
this._flags.Clear(1);
this.ValidateNameValueCollection(this._queryString, RequestValidationSource.QueryString);
}
一看this.ValidateNameValueCollection这个方法名称就知道是干什么的了,验证QueryString数据;那么在什么情况下验证的了?
让我们看看this._flags[1]在什么地方设置的:
public void ValidateInput()
{
if (!this._flags[0x8000])
{
this._flags.Set(0x8000);
this._flags.Set(1);
this._flags.Set(2);
this._flags.Set(4);
this._flags.Set(0x40);
this._flags.Set(0x80);
this._flags.Set(0x100);
this._flags.Set(0x200);
this._flags.Set(8);
}
}
而该方法在ValidateInputIfRequiredByConfig中调用,调用代码
internal void ValidateInputIfRequiredByConfig()
{
.........
if (httpRuntime.RequestValidationMode >= VersionUtil.Framework40)
{
this.ValidateInput();
}
}
我想现在大家都应该明白为什么错题提示让我们把framework改为2.0了吧。应为在4.0后才验证。这种解决问题的方法是关闭验证,那么我们是否可以改变默认的验证规则了?
让我们看看ValidateNameValueCollection
private void ValidateNameValueCollection(NameValueCollection nvc, RequestValidationSource requestCollection)
{
int count = nvc.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
string key = nvc.GetKey(i);
if ((key == null) || !key.StartsWith("__", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
string str2 = nvc.Get(i);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(str2))
{
this.ValidateString(str2, key, requestCollection);
}
}
}
}
private void ValidateString(string value, string collectionKey, RequestValidationSource requestCollection)
{
int num;
value = RemoveNullCharacters(value);
if (!RequestValidator.Current.IsValidRequestString(this.Context, value, requestCollection, collectionKey, out num))
{
string str = collectionKey + "=\"";
int startIndex = num - 10;
if (startIndex <= 0)
{
startIndex = 0;
}
else
{
str = str + "...";
}
int length = num + 20;
if (length >= value.Length)
{
length = value.Length;
str = str + value.Substring(startIndex, length - startIndex) + "\"";
}
else
{
str = str + value.Substring(startIndex, length - startIndex) + "...\"";
}
string requestValidationSourceName = GetRequestValidationSourceName(requestCollection);
throw new HttpRequestValidationException(SR.GetString("Dangerous_input_detected", new object[] { requestValidationSourceName, str }));
}
}
哦?原来一切都明白了,验证是在RequestValidator做的。
public class RequestValidator
{
// Fields
private static RequestValidator _customValidator;
private static readonly Lazy<RequestValidator> _customValidatorResolver = new Lazy<RequestValidator>(new Func<RequestValidator>(RequestValidator.GetCustomValidatorFromConfig));
// Methods
private static RequestValidator GetCustomValidatorFromConfig()
{
HttpRuntimeSection httpRuntime = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().HttpRuntime;
Type userBaseType = ConfigUtil.GetType(httpRuntime.RequestValidationType, "requestValidationType", httpRuntime);
ConfigUtil.CheckBaseType(typeof(RequestValidator), userBaseType, "requestValidationType", httpRuntime);
return (RequestValidator) HttpRuntime.CreatePublicInstance(userBaseType);
}
internal static void InitializeOnFirstRequest()
{
RequestValidator local1 = _customValidatorResolver.Value;
}
private static bool IsAtoZ(char c)
{
return (((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z')) || ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z')));
}
protected internal virtual bool IsValidRequestString(HttpContext context, string value, RequestValidationSource requestValidationSource, string collectionKey, out int validationFailureIndex)
{
if (requestValidationSource == RequestValidationSource.Headers)
{
validationFailureIndex = 0;
return true;
}
return !CrossSiteScriptingValidation.IsDangerousString(value, out validationFailureIndex);
}
// Properties
public static RequestValidator Current
{
get
{
if (_customValidator == null)
{
_customValidator = _customValidatorResolver.Value;
}
return _customValidator;
}
set
{
if (value == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("value");
}
_customValidator = value;
}
}
}
主要的验证方法还是在CrossSiteScriptingValidation.IsDangerousString(value, out validationFailureIndex);而CrossSiteScriptingValidation是一个内部类,无法修改。
让我们看看CrossSiteScriptingValidation类大代码把
internal static class CrossSiteScriptingValidation
{
// Fields
private static char[] startingChars = new char[] { '<', '&' };
// Methods
private static bool IsAtoZ(char c)
{
return (((c >= 'a') && (c <= 'z')) || ((c >= 'A') && (c <= 'Z')));
}
internal static bool IsDangerousString(string s, out int matchIndex)
{
matchIndex = 0;
int startIndex = 0;
while (true)
{
int num2 = s.IndexOfAny(startingChars, startIndex);
if (num2 < 0)
{
return false;
}
if (num2 == (s.Length - 1))
{
return false;
}
matchIndex = num2;
char ch = s[num2];
if (ch != '&')
{
if ((ch == '<') && ((IsAtoZ(s[num2 + 1]) || (s[num2 + 1] == '!')) || ((s[num2 + 1] == '/') || (s[num2 + 1] == '?'))))
{
return true;
}
}
else if (s[num2 + 1] == '#')
{
return true;
}
startIndex = num2 + 1;
}
}
internal static bool IsDangerousUrl(string s)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(s))
{
return false;
}
s = s.Trim();
int length = s.Length;
if (((((length > 4) && ((s[0] == 'h') || (s[0] == 'H'))) && ((s[1] == 't') || (s[1] == 'T'))) && (((s[2] == 't') || (s[2] == 'T')) && ((s[3] == 'p') || (s[3] == 'P')))) && ((s[4] == ':') || (((length > 5) && ((s[4] == 's') || (s[4] == 'S'))) && (s[5] == ':'))))
{
return false;
}
if (s.IndexOf(':') == -1)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
internal static bool IsValidJavascriptId(string id)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(id))
{
return CodeGenerator.IsValidLanguageIndependentIdentifier(id);
}
return true;
}
}
结果我们发现&# <! </ <? <[a-zA-z] 这些情况验证都是通不过的。
所以我们只需要重写RequestValidator就可以了。
例如我们现在需要处理我们现在需要过滤QueryString中k=&...的情况
public class CustRequestValidator : RequestValidator
{
protected override bool IsValidRequestString(HttpContext context, string value, RequestValidationSource requestValidationSource, string collectionKey, out int validationFailureIndex)
{
validationFailureIndex = 0;
//我们现在需要过滤QueryString中k=&...的情况
if (requestValidationSource == RequestValidationSource.QueryString&&collectionKey.Equals("k")&& value.StartsWith("&"))
{
return true;
}
return base.IsValidRequestString(context, value, requestValidationSource, collectionKey, out validationFailureIndex);
}
}
<httpRuntime requestValidationType="MvcApp.CustRequestValidator"/>
个人在这里只是提供一个思想,欢迎大家拍砖!