服务器端的JavaScript脚本 Node.js 使用入门
首先下载node.js,然后解压到E盘,改名为node,然后开始菜单输入cmd,用cd命令切换到nodejs的解压目录:
第一个例子:hello world。
在node目录下建立hello.js文件,然后在里面输入:
var sys = require("sys");
sys.puts("Hello world");
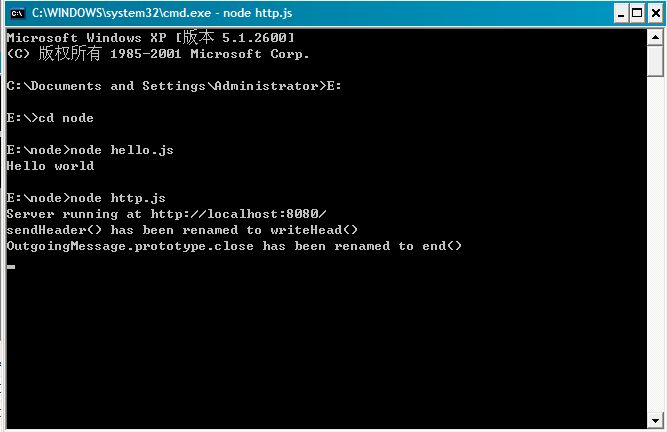
然后我们在命名台中输入命令node hello.js,就能看到命名台输出结果Hello world。
第二个例子:hello world2。
好了,这次我们试从游览器中输出hello world。在node目录下建立http.js,然后输入:
var sys = require("sys"),
http = require("http");
http.createServer(function(request, response) {
response.sendHeader(200, {"Content-Type": "text/html"});
response.write("Hello World!");
response.close();
}).listen(8080);
sys.puts("Server running at http://localhost:8080/");
然后我们在命名台中输入命令node http.js,在浏览器输入http://localhost:8080/

node.js提供一个Buffer类用于转换不同编码的字符串。目前支持三种类型:'ascii','utf8'与'binary'。详见这里
var Buffer = require('buffer').Buffer,
buf = new Buffer(256),
len = buf.write('\u00bd + \u00bc = \u00be', 0);
console.log(len + " bytes: " + buf.toString('utf8', 0, len));
第四个例子:hello world3。
//synopsis.js
//synopsis 摘要, 梗概,大纲
var http = require('http');
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
response.end('Hello World\n');
}).listen(8124);
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:8124/');
前台地址栏:http://localhost:8124/
第五个例子:编译C文件
#include #include int main(){ printf("Hello World!!!"); exit(0); }