asp.net 动态创建TextBox控件及状态数据如何加载
接着上文Asp.net TextBox的TextChanged事件你真的清楚吗? 这里我们来说说状态数据时如何加载的。
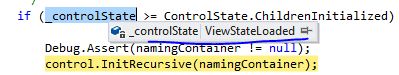
虽然在Control中有调用状态转存的方法,但是这里有一个判断条件 if (_controlState >= ControlState.ViewStateLoaded) 一般的get请求这里的条件是不满足的。
internal enum ControlState
{
Constructed,
FrameworkInitialized,
ChildrenInitialized,
Initialized,
ViewStateLoaded,
Loaded,
PreRendered
}
我们知道在page的ProcessRequest中this.ControlState = ControlState.FrameworkInitialized;ProcessRequestMain方法中在Init后有调用this.InitRecursive(null);在这个方法里面有这么一句_controlState = ControlState.Initialized;,在LoadAllState()方法中有这么一句 base.LoadViewStateRecursive(second.Second);,而LoadViewStateRecursive中又有_controlState = ControlState.ViewStateLoaded这句带代码,所以我们在Page_load中动态条件控件时, if (_controlState >= ControlState.ViewStateLoaded)条件成立,如图:
所以在运行this.form1.Controls.Add(txt);这句以前,txt的值为demo1,
如图
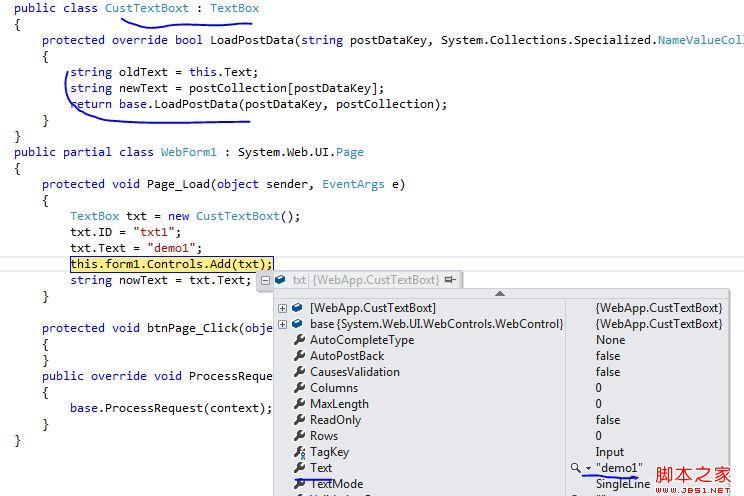
但是运行以后之就发生变化了:

当然这里的txt.Text值也是我上次post过来的旧值,新值是在控件的LoadPostData方法中重新绑定。在默认的LoadViewStateRecursive方法中有一个很重要的判断
internal void LoadViewStateRecursive(object savedState) {
// nothing to do if we have no state
if (savedState == null || flags[disableViewState])
return;
。。。。。。。
_controlState = ControlState.ViewStateLoaded
}
大家看到我上面是一个CustTextBoxt : TextBox控件,如果我们直接添加TextBox控件的话,那么着这里的txt.Text一直都是demo1,可见控件动态添加的时候是否加载状态数据与状态数据的保存有关。而状态数据的保存主要就是SaveViewState完成的,这里我第一次post的时候SaveViewState返回数据:
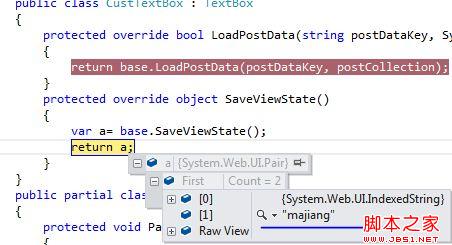
所以第二次能取到上次post过来的数据。
其中与SaveViewState有关的方法主要有:
public class TextBox : WebControl, IPostBackDataHandler, IEditableTextControl {
protected override object SaveViewState() {
if (SaveTextViewState == false) {
ViewState.SetItemDirty("Text", false);
}
return base.SaveViewState();
}
private bool SaveTextViewState {
get {
//
// Must be saved when
// 1. There is a registered event handler for SelectedIndexChanged
// 2. Control is not enabled or visible, because the browser's post data will not include this control
// 3. The instance is a derived instance, which might be overriding the OnTextChanged method
if (TextMode == TextBoxMode.Password) {
return false;
}
if ((Events[EventTextChanged] != null) ||
(IsEnabled == false) ||
(Visible == false) ||
(ReadOnly) ||
(this.GetType() != typeof(TextBox))) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
public class WebControl : Control, IAttributeAccessor {
protected override object SaveViewState() {
Pair myState = null;
// Save values cached out of view state
if (_webControlFlags[disabledDirty]) {
ViewState["Enabled"] = !flags[isWebControlDisabled];
}
if (ControlStyleCreated) {
// the style shares the StateBag of its owner WebControl
// call SaveViewState to let style participate in state management
ControlStyle.SaveViewState();
}
object baseState = base.SaveViewState();
object aState = null;
if (attrState != null) {
aState = attrState.SaveViewState();
}
if (baseState != null || aState != null) {
myState = new Pair(baseState, aState);
}
return myState;
}
}
public class Control : IComponent, IParserAccessor, IUrlResolutionService, IDataBindingsAccessor, IControlBuilderAccessor, IControlDesignerAccessor, IExpressionsAccessor {
protected virtual object SaveViewState() {
// Save values cached out of view state
if (flags[visibleDirty]) {
ViewState["Visible"] = !flags[invisible];
}
if (flags[validateRequestModeDirty]) {
ViewState["ValidateRequestMode"] = (int)ValidateRequestMode;
}
if (_viewState != null)
return _viewState.SaveViewState();
return null;
}
}
public sealed class StateBag : IStateManager, IDictionary {
internal object SaveViewState() {
ArrayList data = null;
if (bag.Count != 0) {
IDictionaryEnumerator e = bag.GetEnumerator();
while (e.MoveNext()) {
StateItem item = (StateItem)(e.Value);
if (item.IsDirty) {
if (data == null) {
data = new ArrayList();
}
#if OBJECTSTATEFORMATTER
data.Add(new IndexedString((string)e.Key));
#else
data.Add(e.Key);
#endif
data.Add(item.Value);
}
}
}
return data;
}
}
到这里我们知道保存状态信息主要是在StateBag 的SaveViewState方法中,这里有一个检查 if (item.IsDirty) ,在TextBox的SaveViewState方法中有一个判断
if (SaveTextViewState == false) {
ViewState.SetItemDirty("Text", false);
}
与它的SaveTextViewState 属性有关。
那么我们可以总结一下:动态创建的控件默认是在被添加的时候加载器状态数据,如果是静态添加的数据那就是LoadAllState来处理状态数据的加载。状态数据的加载与控件的SaveViewState密切相关,如果该方法的返回值为null既没有状态信息,那也不需要加载什么状态信息了。